CFU is a unit used to measure the number of bacteria. You’ve probably seen on the label of your probiotic supplement.
Bacteria have become central to the quest for gut health. So much so that the probiotics market is booming and, by 2025, it is expected to be worth over $74 billion worldwide according to Fortune Business Insights.
Table of contents
So clearly, many people are willing to drop hard-earned cash on live bacterial cultures to boost health, wellbeing, and cognitive performance. So when faced with the choice between probiotics 30 billion CFU or a probiotic 35 billion CFU, the obvious answer is 35, right?
Mathematically yes, 35 is bigger than 30. But what are you actually buying? In this article, we explain the meaning of CFU, what a CFU unit is, and how CFU is calculated, so you can make smart decisions about your probiotic purchases.
☝️TIP☝️Find out what probiotic bacteria are in your gut with the Atlas Microbiome Test.
What is CFU: CFU meaning
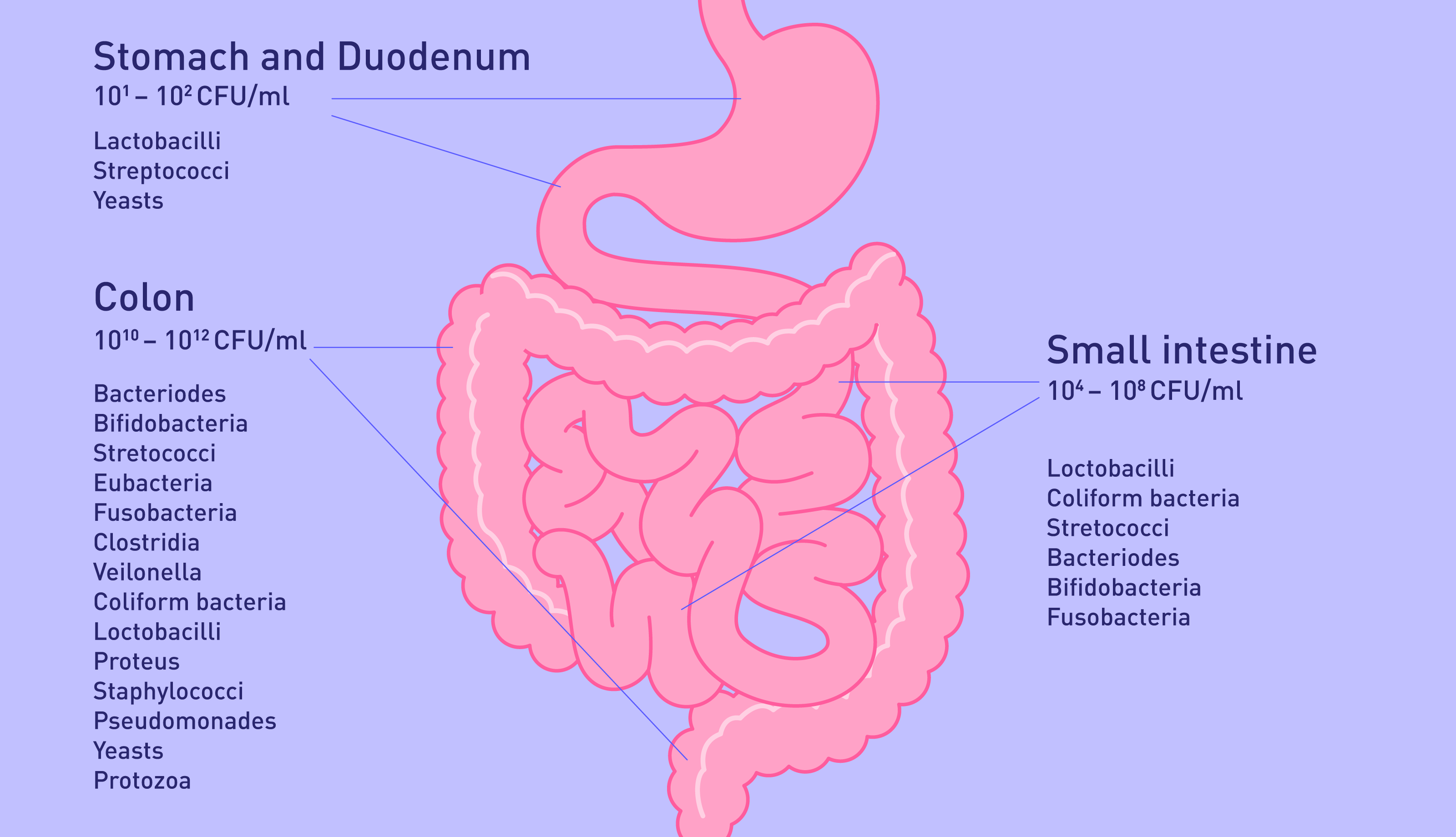
CFU stands for colony-forming unit, a term used to describe the number of viable microorganisms in a probiotic supplement, slice of cheese, kombucha, or any other medium where single-celled organisms thrive (including your stool).
In fact, America’s National Institutes of Health actually recommend buying only probiotics that list the CFU at the end of the product’s shelf life, rather than just the CFU at the time of manufacture because, for probiotics to remain viable, they must be kept in stable conditions.
That’s why bigger CFUs are not a guarantee of high-quality probiotics. Things that could affect the viability of probiotic cells include:
- being transported in a lorry or train in scorching heat
- not being properly and consistently refrigerated
- being stored for long periods before sale
CFU calculation
To give CFU meaning, you have to start in the lab. Colony-forming unit refers to the ability of one cell to reproduce until it forms a colony. Usually, lab techs inoculate a petri dish with a bacterium and then incubate it.
Once a colony has formed, they take a picture of it and then computers get involved. There are different types of software that can calculate CFU ml and CFU g because humans are very bad at counting microscopic cells (and it’s very labour intensive too).
CFU/ml in liquid probiotics
☝️TIP☝️ The CFU/g in probiotic pills and other dry products and supplements is given in grams.
CFU probiotic bacteria
Not every beneficial bacterium is considered probiotic. In fact, this term is specifically reserved for bacteria that have conclusively demonstrated their ability to support and enhance human health in many rigorous studies.
Interestingly, some of them naturally occur in your gut, like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, whether you’re taking a probiotic supplement or not.
| Genus | Species |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | L. rhamnosus |
| L. acidophilus | |
| L. reuteri | |
| L. plantarum | |
| L. fermentum | |
| Bifidobacterium | B. infantis |
| B. longum | |
| B. lactis | |
| B. bifidum | |
| Saccharmyces | S. boulardii |
| Lactococcus | L. lactis |
However, just because you invest in high-quality probiotics with high CFU count doesn’t mean that the probiotic bacteria will stay in your gut. In some cases, their presence in the gut only lasts as long as the person is taking the probiotic.

Don’t worry though because you can support gut health by eating more plant-based foods. Probiotic and beneficial bacteria that live in the human colon thrive on the dietary fibers in fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
The bacteria CFU is a helpful guide when purchasing probiotics, but it contains limited information on the quality of your probiotic. If in doubt, ask a reputable nutritionist for advice on the best brand of probiotics and always remember, your gut health and bacteria need a wholesome diet too.